NIGERIA'S EMPOWERMENT PROGRAMS - What You MUST Know
In a strategic effort to foster national development, the Federal Government of Nigeria has established a comprehensive suite of empowerment programs. These initiatives are designed to address critical socio-economic challenges, with a primary focus on poverty eradication, youth empowerment, and economic diversification.
The Federal Government of Nigeria has launched a diverse portfolio of empowerment programs designed to uplift citizens, eradicate poverty, and promote youth inclusion in national development. These initiatives are structured to address multiple dimensions of economic growth, skills acquisition, and human capital development, with the overarching goal of fostering a self-reliant and economically vibrant society.
Program Objectives and Focus Areas
The government’s empowerment strategy is anchored on five key thematic areas:
1. Job Creation and Skills Development
A central focus of these programs is to expand employment opportunities and equip Nigerians with relevant skills for today’s economy.
- Programs such as the National Directorate of Employment (NDE), Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET), 3 Million Technical Talent (3MTT) program, and Skill-Up Artisans (SUPA) are aimed at producing a skilled workforce capable of driving industrial and digital transformation.
- These initiatives target technical, vocational, and digital skills training, enabling beneficiaries to become employable or self-sufficient entrepreneurs in various sectors.
2. Entrepreneurship and Access to Finance
The government recognizes that sustainable development is rooted in entrepreneurial growth and innovation.
- Programs such as the Nigeria Youth Investment Fund (NYIF) and Youth Entrepreneurship & Innovation Development Plan (YEIDEP) provide financial support, startup grants, and business mentorship for young entrepreneurs.
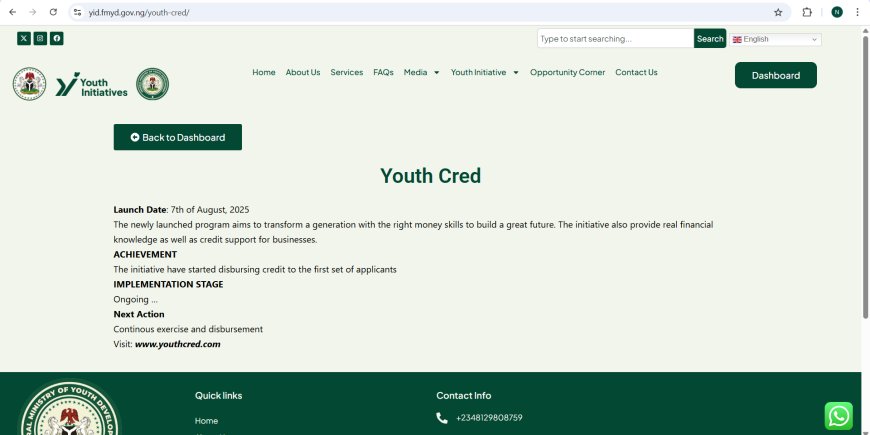
- Institutions like the Bank of Industry (BOI) and initiatives such as the Creative Economy Development Fund (CEDF) and Youth Credit Scheme expand access to credit facilities for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), as well as for individuals in the creative, agricultural, and technology sectors.
- Collectively, these programs promote financial inclusion, job creation, and economic diversification.
3. Welfare and Social Support Systems
Social protection and welfare initiatives are critical in addressing the needs of vulnerable groups.
- Programs like the Presidential Conditional Grant Scheme (PCGS) support low-income traders, artisans, and small business owners with non-repayable financial assistance.
- The Nigerian Education Loan Fund (NELFUND) and Tertiary Institution Student Support Fund (TISSF) are designed to ensure equitable access to higher education and prevent financial hardship from hindering academic pursuits.
- The Renewed Hope Cities and Estates initiative and the Federal Government Staff Housing Loans Board (FGSHLB) focus on affordable housing and improved living standards for civil servants and low-income earners.
- The government has also emphasized consumer credit accessibility to stimulate economic participation among citizens.
4. Work Placement and Employability Enhancement
Bridging the gap between education and employment remains a key priority.
- The Nigeria Jubilee Fellows Programme (NJFP) provides graduate placement opportunities, offering structured on-the-job experience to enhance employability.
- Through such initiatives, the government aims to reduce graduate unemployment and ensure that young professionals are adequately prepared for competitive labor markets.
5. Sectoral and Agricultural Support
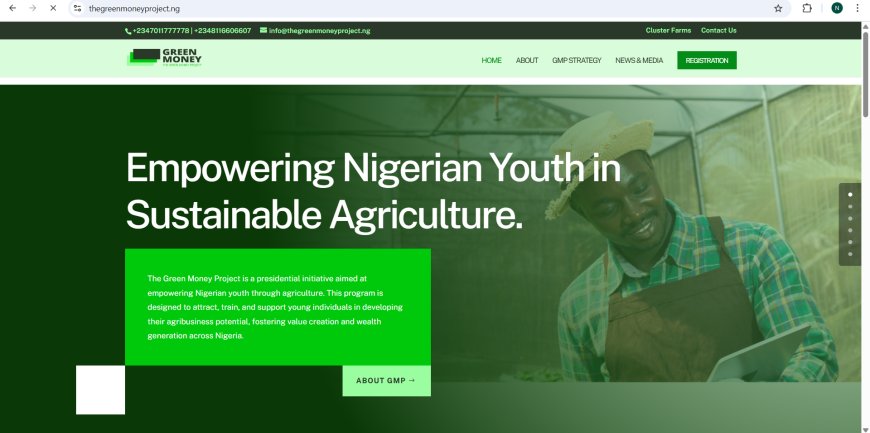
Recognizing agriculture as a cornerstone of economic growth, several programs target agricultural development and green investment.
- Initiatives such as the Agricultural Credit Support Scheme (ACSS) and the Green Money Project encourage food production, agro-processing, and sustainable agricultural practices.
- These programs also align with national goals for food security, climate resilience, and rural development.
Key Programs at a Glance
Some of the most impactful initiatives under this empowerment framework include:
NDE, TVET, 3MTT, SUPA, YEIDEP, NYIF, NJFP, PCGS, CEDF, Green Money Project, Youth Credit Scheme, NELFUND, TISSF, and BOI.
Implementation and Operational Challenges
Despite their potential, the success of these programs is constrained by several systemic and operational issues that hinder full realization of objectives.
1. Lack of Implementation Timeliness and Clarity
A major concern across several initiatives is the uncertainty surrounding their implementation timelines and communication structure.
- Many programs have completed registration phases without clear follow-up processes or published results on beneficiary selection.
- Applicants often face prolonged waiting periods without updates, leading to confusion about whether disbursement or training phases have commenced.
- Some citizens report having incurred personal costs (e.g., opening program-specific bank accounts, completing online verifications, or traveling for documentation) without receiving subsequent feedback or benefits.
This lack of transparency and predictable execution has eroded public trust and created frustration among would-be beneficiaries who see these programs as promises without tangible outcomes.
2. Data Management and Verification Gaps
Many initiatives face challenges in verifying the authenticity of applicants, resulting in delays, duplication of records, or fraud risks. Weak data coordination among agencies has also made tracking and evaluation difficult.
3. Limited Public Awareness and Outreach
While the government has launched numerous empowerment schemes, awareness and accessibility remain limited in rural areas. Many citizens are either unaware of available opportunities or lack digital literacy to complete online applications effectively.
4. Funding and Sustainability Concerns
Some programs depend on periodic budget allocations or donor support, making them vulnerable to funding shortfalls that disrupt continuity and scalability.
Conclusion
The Federal Government’s empowerment and development programs represent a bold and inclusive approach to addressing unemployment, poverty, and economic inequality in Nigeria. However, to achieve maximum impact, greater emphasis must be placed on implementation transparency, accountability, and sustained communication with the public. Streamlined coordination across ministries and agencies, coupled with real-time updates for applicants, will ensure that these initiatives fulfill their intended purpose—to empower Nigerians and build a stronger, more resilient economy.